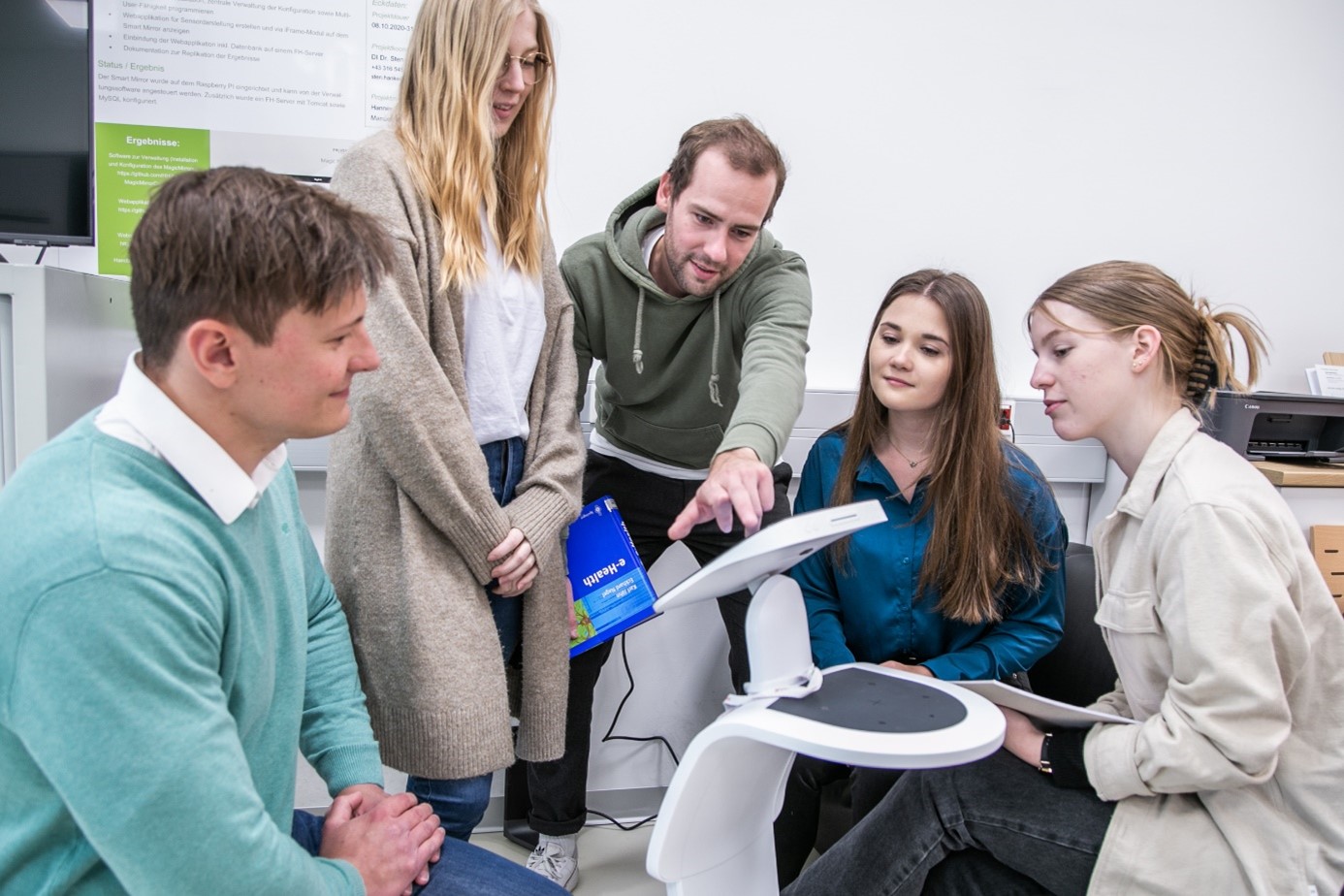
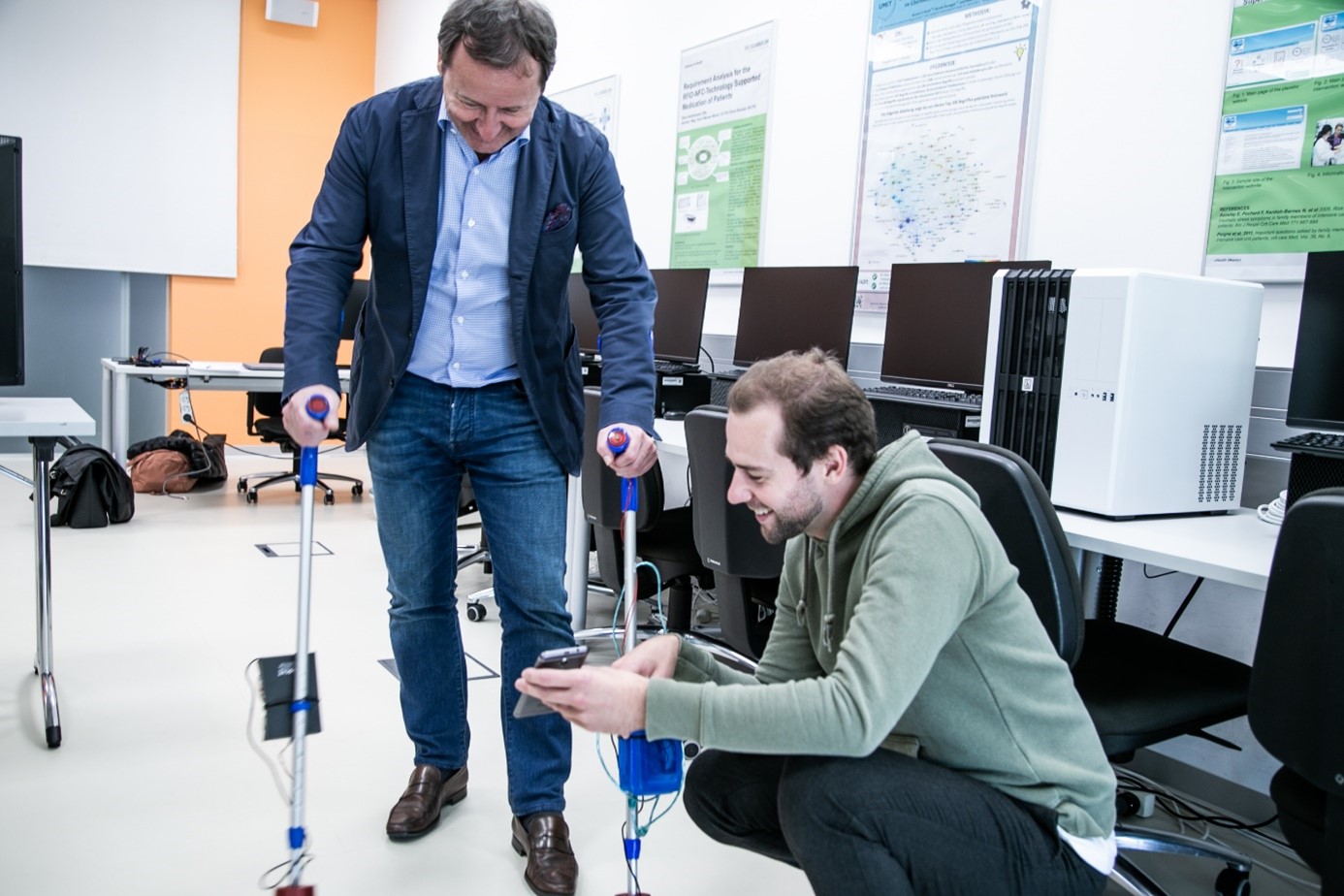
The Smart Care Laboratory is designed as a living lab and thus makes an important contribution to the realization of the mission statement of the eHealth Institute:
“We traintomorrow’s eHealth experts who will help shape the digital transformation of the healthcare sector in order to improve people’s quality of life.”
In line with the teaching priorities of the eHealth Institute, the Smart Care Laboratory is intended to create an opportunity to practice complex theoretical teaching content in a practice-oriented, hands-on environment.
The Smart Care Laboratory is used in many ways:
- Healthy Aging – Active (Ambient) Assisted Living: Assistive technologies in one’s own four walls can be an alternative to the nursing home for many people. The research field ranges from smart home applications that support the performance of everyday activities, sensor-supported monitoring and remote monitoring of chronically ill people to care robots.
- Smart Health Care – Wearables in healthcare: Sensors, which are becoming ever smaller and cheaper, as well as smart applications based on artificial intelligence form the technological basis for efficient and high-quality diagnostic and therapy processes. With the use of new information and communication technologies, it is possible to analyze existing processes and to optimize them with regard to the use of new technologies.
- Documentation standards and data management in healthcare – HL7, CDISC, DRG: Documentation standards such as HL7 or CDISC are intended to increase interoperability and thus lead to higher efficiency and an increase in data quality. When it comes to routine clinical data, there is a great need for coordination between the different sectors of the health and social care system. Medical and nursing discharge letters, findings or medication data must be exchangeable between hospitals, outpatient clinics and nursing homes.